API Authentication
There are many types of API authentication, each with their own benefits and tradeoffs.
A few of the main ones are:
- HTTP
- API Key
- JWT
- OAuth
Types of API Authentication
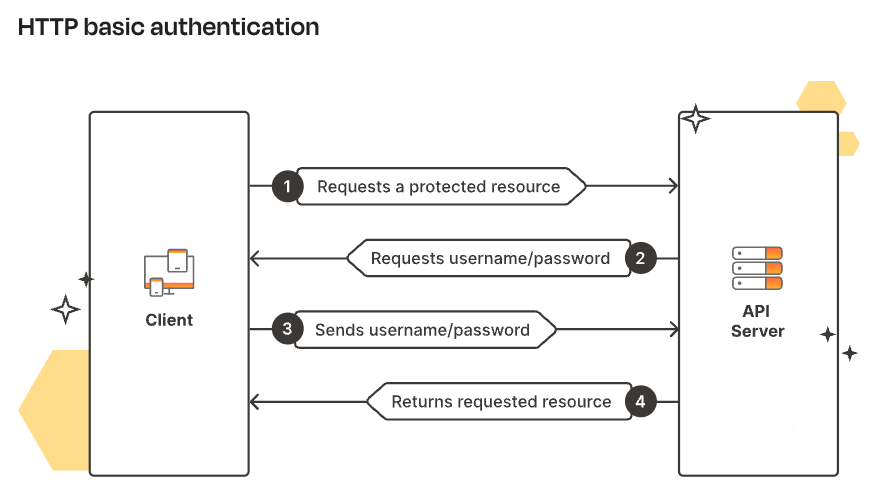
1. HTTP Authentication
The most basic type of authentication. It involves sending the username and password as a pair in the Authorization header.
The credentials are encoded using Base64, but not hashed or encrypted, making it less secure unless used over HTTPS.
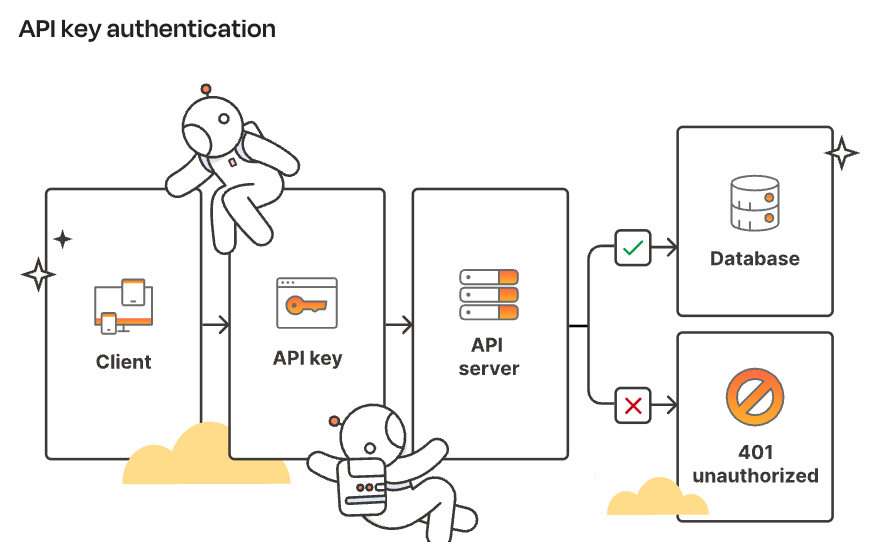
2. API Key Authentication
A unique identifier that an API provider gives to its users to control access and monitor usage.
The API key must be sent with every request — either as a request header or cookie.
It must be used with HTTPS to ensure a secure connection.
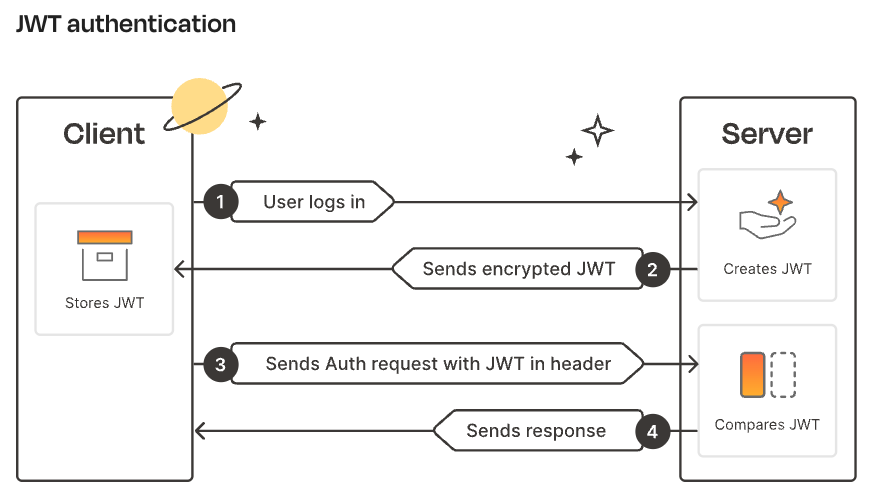
3. JWT (JSON Web Token)
A stateless mechanism for API authentication.
- When a user logs into an application, the API server generates a JWT and sends it to the client.
- The client sends this JWT back in subsequent requests.
- The server validates the JWT to authenticate the request.
4. OAuth Authentication
OAuth is a token-based authentication method where users grant third-party applications access to their accounts without sharing login credentials.
API Authentication vs. API Authorization
- Authentication: Verifying a user's identity.
- Authorization: Verifying a user's permissions to access specific tasks or resources within the API.
Best Practices
- Use a well-established API authentication framework.
- Choose the method that best suits your use case.
- Implement two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible.
- Always use HTTPS for secure communication.
- Enable logging and monitoring to track API usage and detect anomalies.